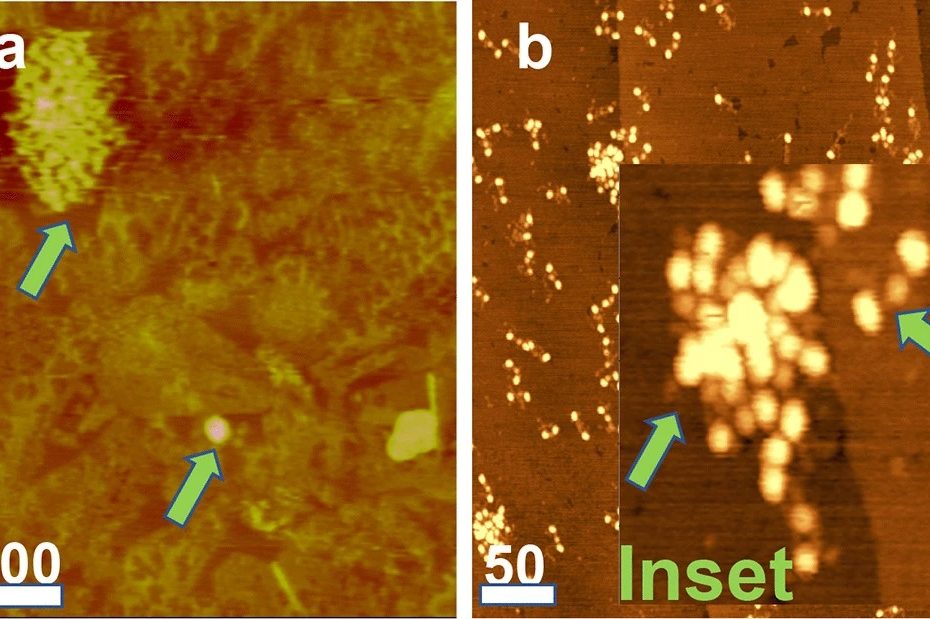
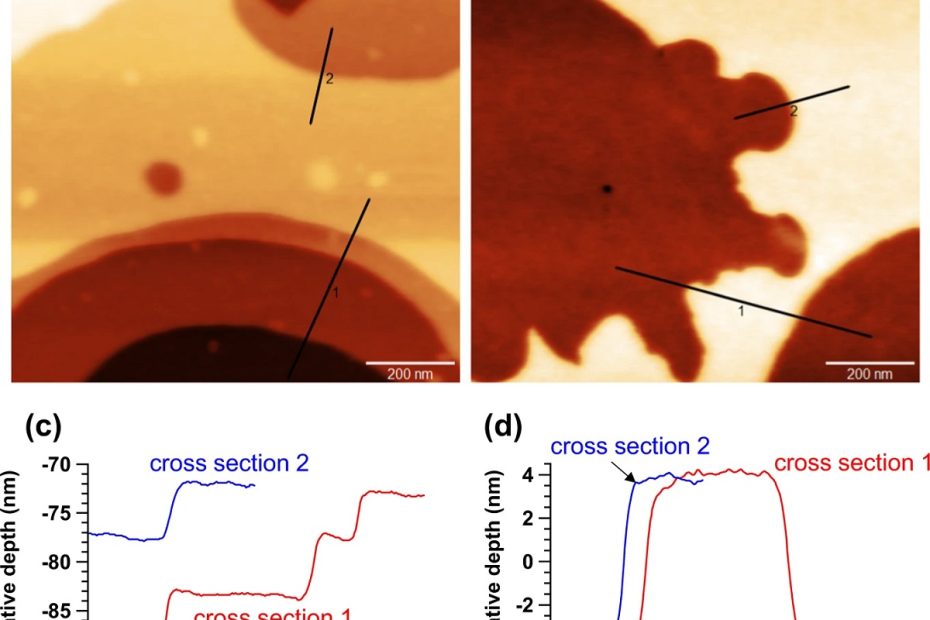
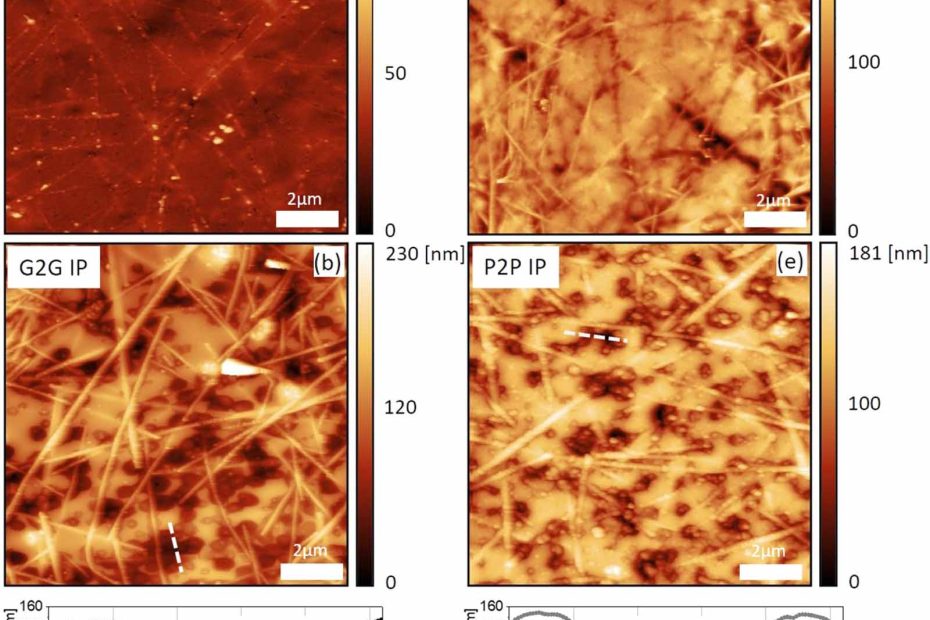
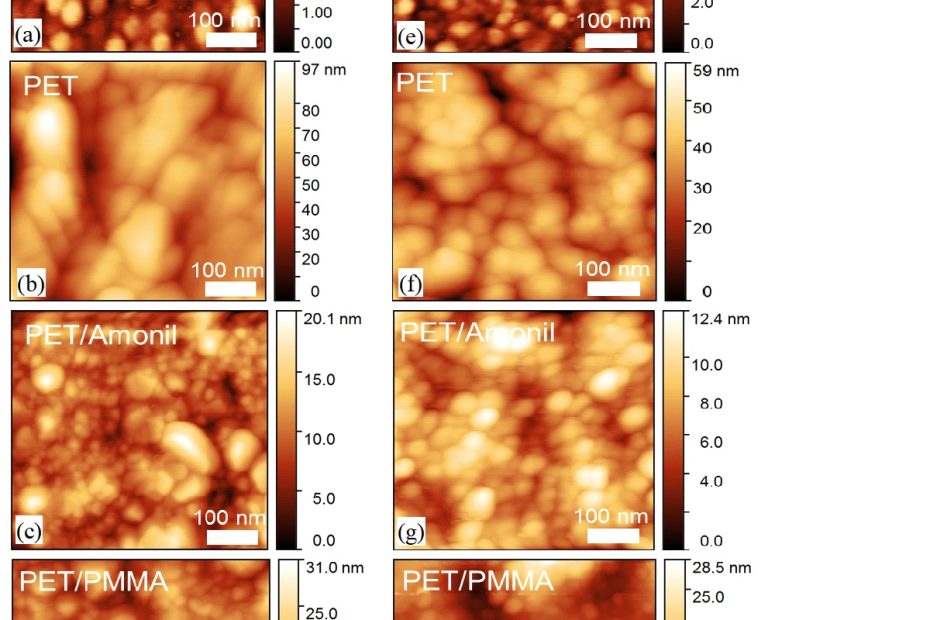
Transparent electrodes based on molybdenum-titanium-oxide with increased water stability for use as hole-transport/hole-injection components
The application of molybdenum oxide layers in electronic devices like solar cells and organic light emitting diodes (LEDs) has expanded considerably. * Dielectric/metal/dielectric (DMD) transparent… Read More »Transparent electrodes based on molybdenum-titanium-oxide with increased water stability for use as hole-transport/hole-injection components