Caffeine is widely present in food and drinks, such as teas and coffees, being also part of some currently commercialized medicines, but despite its enhancement on several functions of human body, its exceeding use can promote many health problems.*
The paper “Electrodeposition of 4-Benzenesulfonic Acid onto a Graphite-Epoxy Composite Electrode for the Enhanced Voltammetric Determination of Caffeine in Beverages” by Leonardo de A. Furtado, Mariana C. de O. Gonçalves, Carlos V. M. Inocêncio, Edilson M. Pinto, Daniela de L. Martins and Felipe S. Semaan presents a new method for the determination of caffeine through voltammetry using the square wave technique.*
In order to develop new fast approaches for the caffeine sensing, graphite-epoxy composite electrodes (GECE) were used as substrate, being modified by different diazonium salts, synthetized as their tetraflouroborate salts.
The paper by Leonardo de A. Furtado et al. presents the modification procedure, the study of pH used for buffer solution’s choice, and an electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) study of all modifications in presence and absence of the analyte, as well, analytical comparison with bare and modified electrodes for caffeine determination.*
Atomic Force Microscopy images were measured to evaluate the surface topography and roughness, before and after the modification. The AFM images showed a decrease in the surface roughness after modification of the electrodes with diazonium salts. Based on this data, it is possible to infer that the modification made a more homogeneous surface compared with the bare electrode.* NANOSENSORS™ PointProbe® Plus PPP-NCLR AFM probes were used.
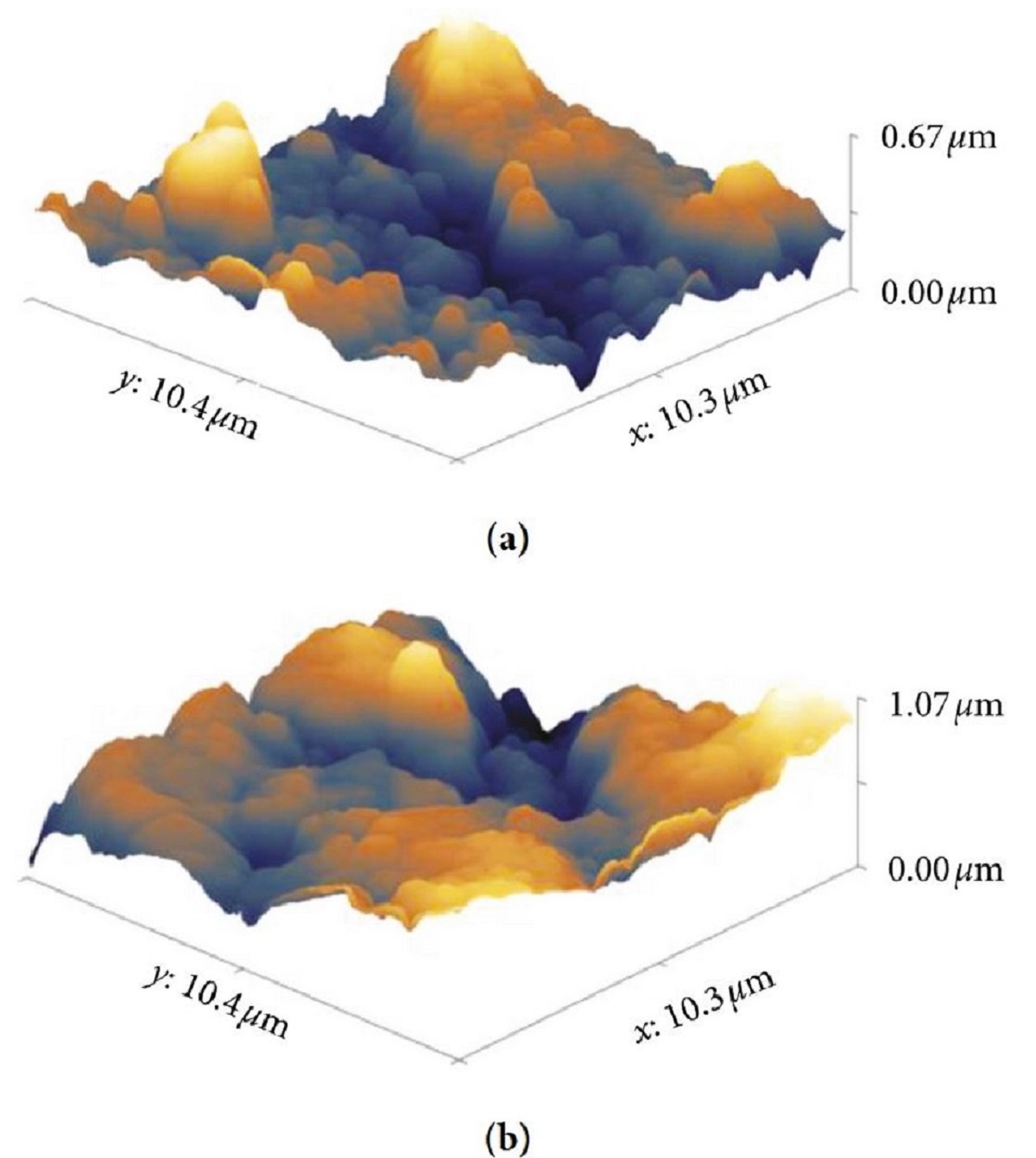
Figure 5 from “Electrodeposition of 4-Benzenesulfonic Acid onto a Graphite-Epoxy Composite Electrode for the Enhanced Voltammetric Determination of Caffeine in Beverages” by Leonardo de A. Furtado et al.:
Surface topography via AFM of (a) bare electrode and (b) electrode modified with 4-benzenesulfonic acid.
*Leonardo de A. Furtado, Mariana C. de O. Gonçalves, Carlos V. M. Inocêncio, Edilson M. Pinto, Daniela de L. Martins and Felipe S. Semaan
Electrodeposition of 4-Benzenesulfonic Acid onto a Graphite-Epoxy Composite Electrode for the Enhanced Voltammetric Determination of Caffeine in Beverages
Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry, Volume 2019, Article ID 8596484, 11 pages
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8596484
Please follow this external link to read the full article: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jamc/2019/8596484/
Open Access: The article “Electrodeposition of 4-Benzenesulfonic Acid onto a Graphite-Epoxy Composite Electrode for the Enhanced Voltammetric Determination of Caffeine in Beverages” by Leonardo de A. Furtado, Mariana C. de O. Gonçalves, Carlos V. M. Inocêncio, Edilson M. Pinto, Daniela de L. Martins and Felipe S. Semaan which is cited above is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.