The molecularly imprinted polymer ( MIP ) technology is currently experiencing a rapid development due to the limitations of natural recognition elements such antibodies or aptamers.*
However, neither MIP strategies are limitless. Therefore, the combination of these powerful tools in a specific immunoassay may bring highly selective approach.*
In their article “cdS quantum dots-based immunoassay combined with particle imprinted polymer technology and laser ablation icp-MS as a versatile tool for protein detection” Tereza Vaneckova, Jaroslava Bezdekova, Michaela Tvrdonova, Marcela Vlcnovska, Veronika Novotna, Jan Neuman, Aneta Stossova, Viktor Kanicky, Vojtech Adam, Marketa Vaculovicova and Tomas Vaculovic introduce a MIP-based pseudo-immunoassay using NP-labelled antibody recognition and couple it with the sensitive detection technique laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry ( LA-ICP-MS ).*
Two approaches of specific recognition were tested.
The first one was based on the immunolabelling of the analyte captured by the MIP layer.
The second approach involved immunolabelling of the analyte as a first step and the resulting QD-AB-AG complex was captured by MIP and further analyzed.
The double-selective approach comprising of the specific immunolabelling reaction combined with isolation by MIP together with the LA-ICP-MS detection represents a viable approach of the IgG detection from a complex sample (LOD 4.2 μg and 1.6 μg, respectively) available for many exciting applications.
Considering the overall time of the LA-ICP-MS analysis not exceeding 23 s (scan speed of 2000 μm/s), LA-ICP-MS is a promising technology to be used in future in conjunction with MIP technology.*
The sample surface was analyzed using SEM with integrated AFM. Correlative Probe and Electron Microscopy (CPEM)48 was used for the surface analysis allowing simultaneous acquisition of SEM and AFM images at the same place in the same coordinate system. The SEM contrast is sensitive to the sample composition, while the AFM provides real surface topography. The accelerating voltage of 5 kV, beam current of 13 pA and SE detector was used for SEM imaging.*
NANOSENSORS self-sensing self-actuating Akiyama probes in tapping mode were used for the AFM measurement.
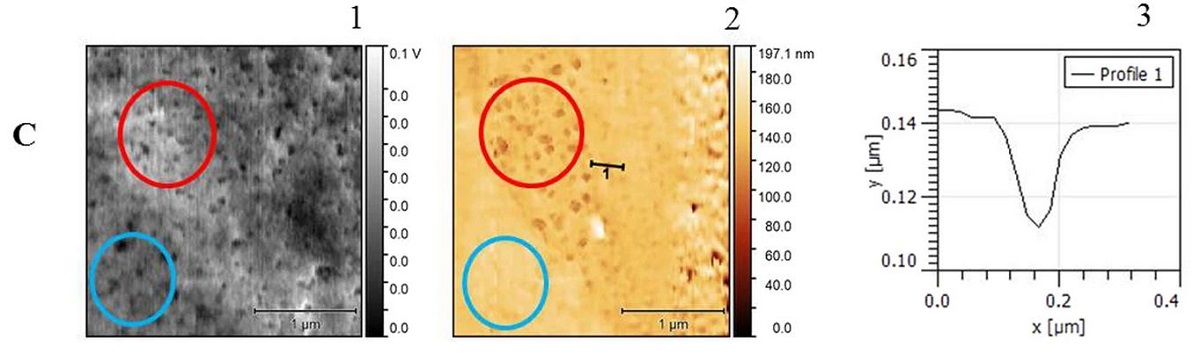
Figure 3 c from: «CdS quantum dots-based immunoassay combined with particle imprinted polymer technology and laser ablation ICP-MS as a versatile tool for protein detection» by Tereza Vaneckova et al.
(C) Correlative Probe and Electron Microscopy (CPEM) imaging of MIP layer with imprinted QD-AB conjugate. 1 – SEM image, 2 – AFM image of the same area and sample in the same coordinate system. 3 – profile of a well formed due to the imprinting process.
In Fig. 3C, the surface visualization obtained by Correlative Probe and Electron Microscopy (CPEM) is shown. SEM image (1) and AFM image (2) were obtained simultaneously from the same region of the sample. Mainly two regions of the surface are of our interest (red and blue circle). Even though SEM image shows similar contrast of both regions, AFM imaging clearly confirms differences between the flat surface (blue circle) and wells formed due to the imprinting process (red circle). Profile of one of the wells is shown in (3). *
*Tereza Vaneckova, Jaroslava Bezdekova, Michaela Tvrdonova, Marcela Vlcnovska, Veronika Novotna, Jan Neuman, Aneta Stossova, Viktor Kanicky, Vojtech Adam, Marketa Vaculovicova, Tomas Vaculovic
cdS quantum dots-based immunoassay combined with particle imprinted polymer technology and laser ablation icp-MS as a versatile tool for protein detection
nature, Scientific Reports, (2019) 9:11840
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48290-2
Please follow this external link to read the full article: https://rdcu.be/bXosX
Open Access The article “CdS quantum dots-based immunoassay combined with particle imprinted polymer technology and laser ablation ICP-MS as a versatile tool for protein detection” by Tereza Vaneckova, Jaroslava Bezdekova, Michaela Tvrdonova, Marcela Vlcnovska, Veronika Novotna, Jan Neuman, Aneta Stossova, Viktor Kanicky, Vojtech Adam, Marketa Vaculovicova and Tomas Vaculovic is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.